Configuration Management Software
Inside Configuration Management Software Solutions :
What is Configuration Management (CM)?
While there are many industry-specific definitions of Configuration Management (CM), a good general definition is the application of resources, methodologies, processes, best practices, standards, governance policies, and configuration management software tools to establish and maintain consistency and traceability between product requirements, the actual product as manufactured and serviced over its lifecycle, and associated product data for all the creators, users, revisers, and custodians of this information.
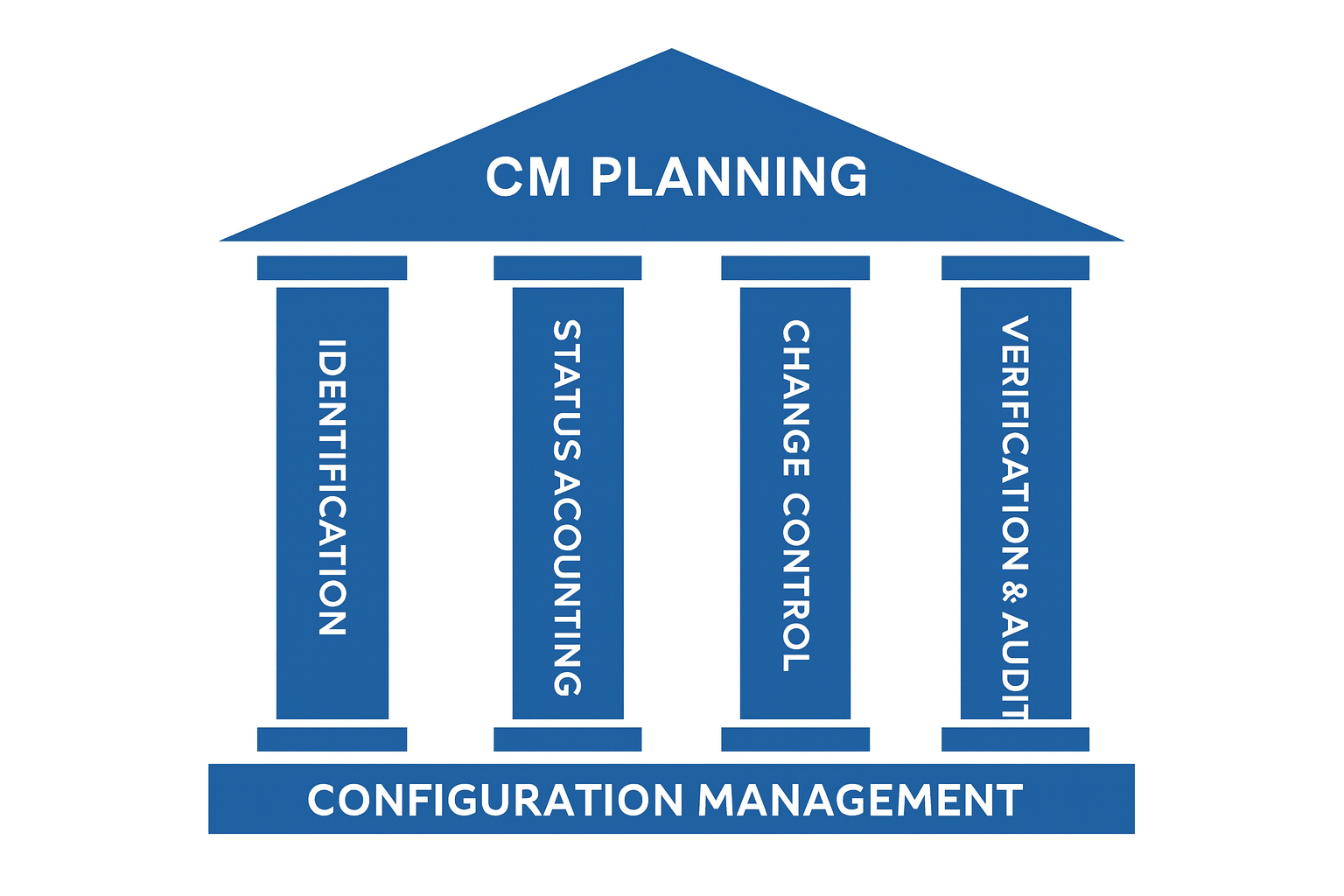
Regardless of the industry or application, configuration management methods, processes and software must support the fundamental pillars of CM including configuration identification, configuration status accounting, configuration change control, and configuration verification and audits.
Functions that Configuration Management Software Supports
It is not uncommon that each industry-specific use of configuration management may have its own set of objectives, requirements, standards and best practices. One example is from the ISO 10007 standard which states the objective of CM is to “document and provide full visibility of the product’s present configuration and the status of achievement of its physical and functional requirements, such that everyone working on the project at any time in its life cycle is using correct and accurate information.”
CLICK HERE for more information about CM as a discipline, including references to industry standards, old and new, such as CMII, ANSI/EIA 649, SAE 649B-1, MIL-STD-973, and EIA 836B.
How is Configuration Management used?
The practice of configuration management is applicable to physical products, complete systems, processes, and services, as well as to their software, data and documentation. This includes configuration management (CM) of hardware, software and firmware used in parts, products, product portfolios, equipment, systems, IT devices, and other assets.
More recently, configuration management has developed a role in model-based systems engineering (MBSE) including the management of virtual digital twin representations.
For physical products, CM helps to manage the configurations of discrete manufactured products including all the hardware, firmware and software components. Hardware configuration management is explicitly focused on managing the hardware components of products, component parts, equipment, systems, or networks. To learn more about an example of how Hardware CM software can be used, watch this short Configuration Management Software video below or on CMstat’s YouTube Channel.
The use of configuration management software becomes more necessary and powerful when employed to manage the configuration over the lifecycle of product variants, product line portfolios, assemblies, mock-ups, test models, virtual twins, systems and even networks of systems. This includes managing configuration data at the component, product, or system level that may be accessed in requirements specifications, contracting procurement, engineering changes, product documentation, work orders, maintenance history, installation instructions, repair manuals, quality inspection, safety records, and compliance certifications. As such, the best practices of CM are applicable to not only physical products but all of their related paper, digital, and virtual records that become a long winding digital thread.
The historic use case of CM was to support new product development, design engineering and manufacturing. CM is considered a must-have fundamental capability before bill-of-materials (BOM) management, release management, and change management can be undertaken at the product or systems engineering levels. For these design engineering-centric uses, CM capabilities are often provided by Product Data Management (PDM) solutions as part of a Product Innovation Platform (PIP) architecture or Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) business strategy.
However, the use of CM beyond product engineering design and manufacturing has become equally important in managing deployed equipment and assets over their long lifecycles of use, repair, and refurbishing. Learn more about these uses of CM in Asset Lifecyle Configuration Management.
What are applications for CM software?
There are many different application categories for Configuration Management software solutions because of the large range of industries and the unique needs and standards each industry has for CM solutions. These application areas include:
Software Configuration Management
System and System-of-Systems Configuration Management
Product Structure Configuration Management
Product Data Configuration Management
Model Based Systems Engineering Configuration Management
Requirements Configuration Management
Process Configuration Management
Test Bed Configuration Management
Asset Configuration Management
Network Configuration Management
In-Service Configuration Management
As-Built, As-Deployed, As-Maintained, and As-Repaired Configuration Management
Operator-Dependent Configuration Management
IT Infrastructure Library Configuration Management
Configuration Lifecycle Management
It is rare if not impossible to find most of these CM applications explicitly supported by any one engineering PDM software or enterprise PLM system. Thankfully, best-of-class industry-focused CM solutions like CMstat’s EPOCH CM do exist that deliver the CM functionality these applications require within a standard commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) software product. To see firsthand how CMstat software supports these applications request a Demonstration.
What are important capabilities of Configuration Management software?
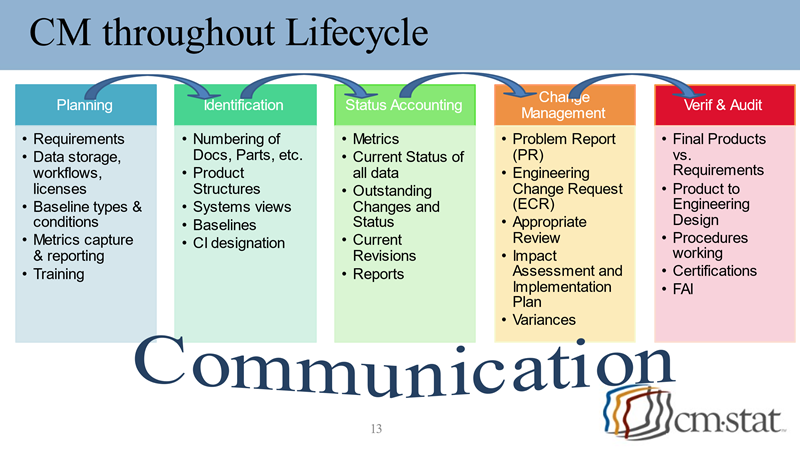
Configuration Management Software Capabilities Span Communications Across the Product Lifecycle
Regardless of the intended application of a Configuration Management software solution, it must support the five high-level tenets of CM: configuration planning, configuration identification, configuration control, configuration status accounting, and configuration traceability and audits. These capabilities are typically delivered by a set of core CM functions which are enabled by the following CM software features:
Product Structure Management
Baseline Identification & Specification
Configuration Item Management
Configuration Data Management
Configuration Identification & Control
Configuration Status Accounting
Configuration Rules
CM Processes & Workflows
CMII and EIA 649 Standards Implementation
Bill of Material (BOM) Management
Change Management & Reporting
Change Implementation and Impact Analysis
Change Effectivity Analysis & Management
CAD-Independent CM
Tracking of As-Designed, As-Built, As-Maintained Configurations
Warranty Management
Document Management
Configuration Planning Management
Reviews, Audits, and Compliance Reporting
LEARN MORE how CMstat’s latest product, EPOCH CM, offers the deep functionality to support all of the capabilities required of a comprehensive CM solution.
Who uses CM software and what are the benefits?
While the use of configuration managed first arose from the A&D industry, there are now numerous industries where the complexity of products, along with their operation and maintenance, require CM tools. Learn more about the different needs within several of these industries HERE.
The users of CM software, and consumers of the data generated, within these industries can be found in many organizations across the enterprise. These groups can include contracts, requirements, procurement, design engineering, manufacturing, supply chain, logistics, quality assurance, test, regulatory compliance, technical publications, service, maintenance, and overhaul. To explore the benefits that CM provides these departments visit EPOCH CM Benefits.
Specific CM user roles within these groups often include design engineers, system engineers, data managers, configuration specialists, procurement buyers, quality inspectors, logistic engineers, compliance officers, technical writers, service technicians, and maintenance personnel. To read more about who really are the users of CM read this article CMsights on CM Users.
Receive CMsights
Subscribe to CMsights News for the latest updates from CMstat on Configuration Management, Data Management, EPOCH CM, and EPOCH DM.
Request a Demo
See how EPOCH CM and EPOCH DM support industry standards and best practices in Configuration Management and Data Management